.NET 筆記
概述
先簡單有個概念,來個 wiki 上的圖

- 高階語言被編譯成 CIL (Common Intermediate Language)
- CLR (Common Language Runtime) 透過 JIT (Just-In-Time) 即時地把 CIL 編譯成 Machine Code 執行
跟 Java 蠻像的,可以看參考資料 4
| .Net | Java |
|---|---|
| CIL | Bytecode |
| CLI (Common Language Infrastructure) | JVM (注意這邊的 JVM 是規範而不是某個實作) |
| CLR (CLI 的其中一個實作) | J9 VM |
而參考資料 1 中提到
針對執行階段所開發的程式碼稱為 Managed 程式碼,而不針對執行階段所開發的程式碼稱為 Unmanaged 程式碼。
在 Windows 上,跑在 CLR 的程式碼就是 Managed 程式碼 (被 CLR 所管理),實際上管理了什麼東西,其一就是記憶體,例如提供 GC (Garbage Collection) 機制
從 Managed code 呼叫 Unmanaged libraries 需要用到 P/invoke 技術,這邊的技術細節先挖一個坑,之後另外寫文章說明
參考資料 3 中提到
以下是編譯到執行的簡略步驟:
C#編譯器幫我們撰寫的C#程式進行編譯
過程中會進行語法檢查與型別變數的安全檢查(例如避免int存取double發生型別不一致)
編譯器會編譯出IL與程式相關資料(稱為中繼資料,一種表示程式本身方法、類別、變數等自我描述資料)包裝成exe或dll檔等這類Windows可執行檔(PE檔)
PE檔的開頭會要求Windows把程式執行權轉交給MSCorEE.dll(.NET Framework的檔案)
MSCorEE.dll的CorExeMain函式會建立通用運行環境(CLR)
CLR會看相關資料準備需要的內容,例如會用到.NET類別庫的那些功能。 當執行到正要用的功能時進行JIT編譯轉成機器碼。
所以可以用有沒有 Import 到 mscoree.dll 來判斷是否為 .NET CIL 程式
參考資料 8 提到
After the PE and COFF headers come the data directories; each directory specifies the RVA (first 4 bytes) and size (next 4 bytes) of various important parts of the executable. The only relevant ones are the 2nd (Import table), 13th (Import Address table), and 15th (CLI header). The Import and Import Address table are only used by the startup stub, so we will look at those later on. The 15th points to the CLI header, where the CLR-specific metadata begins.
The 15th entry (at offset 0x168) contains the RVA and size of the CLI header inside the .text section.
參考 PE Format
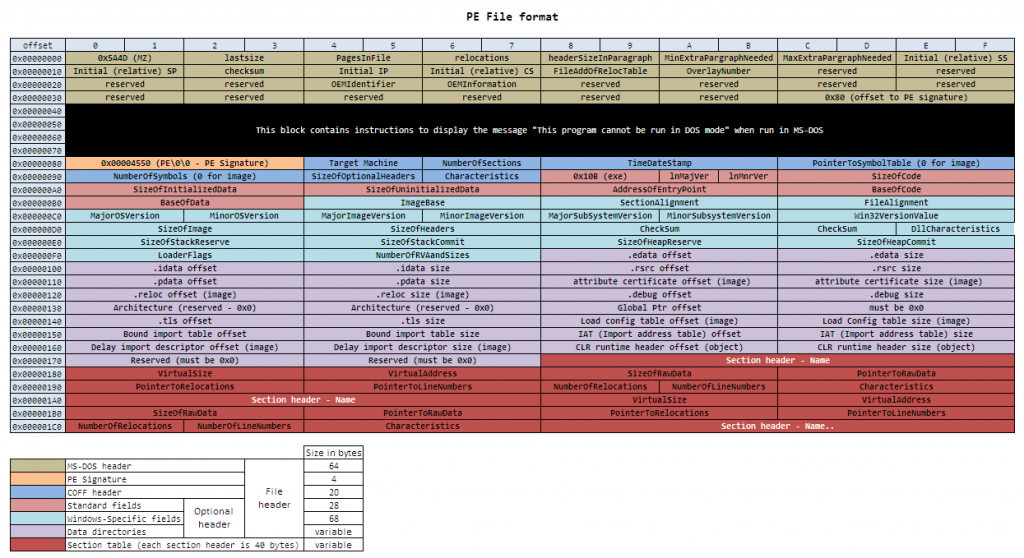
在 offset 0x168 是紀錄 CLR header 的位置及大小
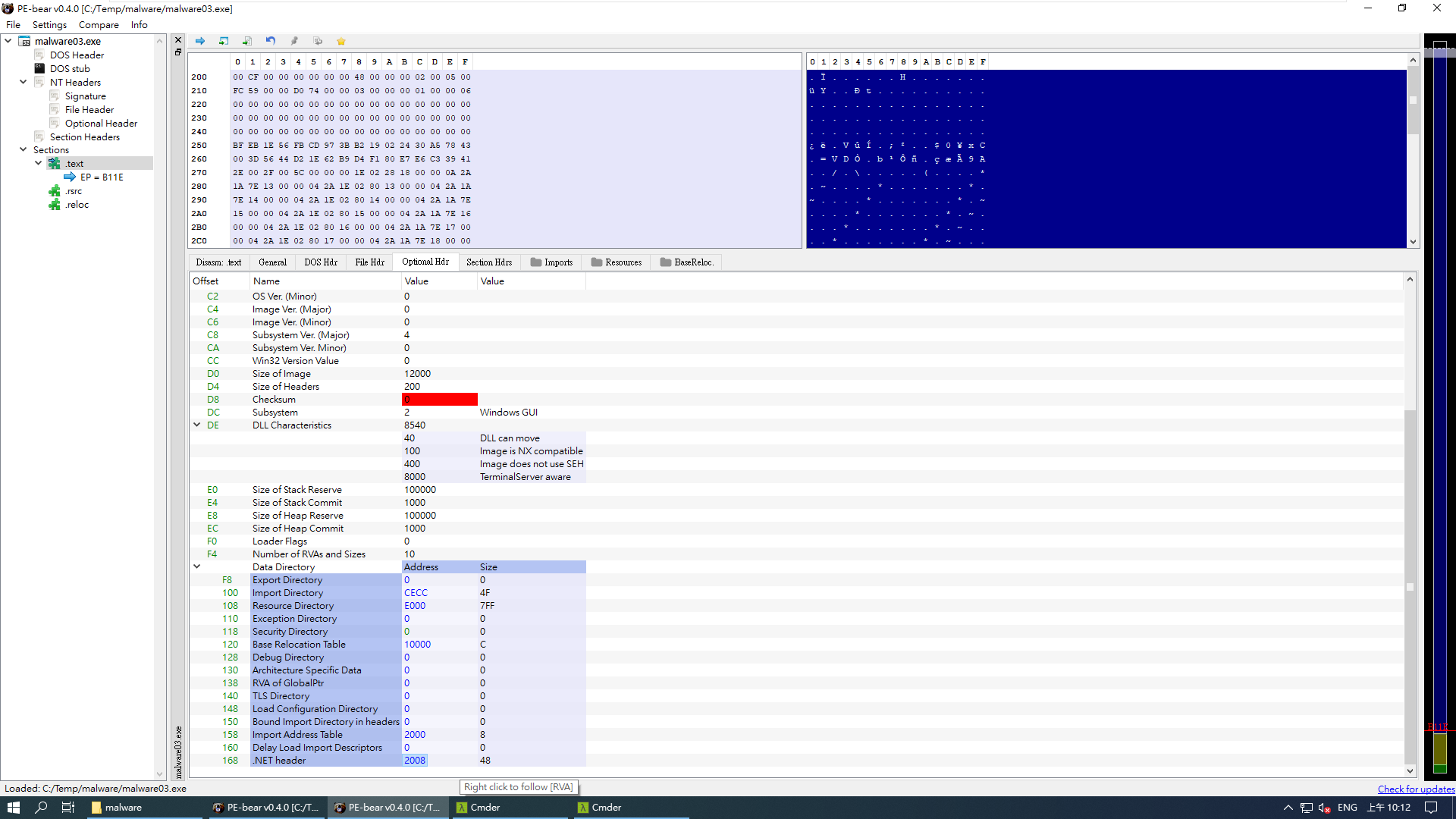 在 PE-bear 這個工具中,CLR runtime header offset & size 是看底下的 .NET header
在 PE-bear 這個工具中,CLR runtime header offset & size 是看底下的 .NET header
透過 .NET header offset (RVA) - .text RVA + .text Pointer of Raw Data 就能 locate 到 .NET header
這部分先開一個 PE format 的坑,以後寫文章來記錄
JIT (Just-In-Time)
而 JIT 的概念可以看看 JIT 在 Javascript Engine 的應用
從簡報中的圖解來看

配合參考資料 6:
實現JIT編譯器的系統通常會不斷地分析正在執行的代碼,並確定代碼的某些部分,在這些部分中,編譯或重新編譯所獲得的加速將超過編譯該代碼的開銷。
在 JIT Compiler 將中間碼轉換為 Machine code 執行後,JIT Compiler 仍舊在分析 Machine code,當發現某一段 code 很常被執行時,JIT Compiler 就會優化此段 code,並在優化過的 code 產生完畢後噴射回記憶體上取代原來的 code 並繼續執行。
不難理解這實際上是個在機器碼產生的速度與效率之間的 trade-off,在程式未執行前就將所有程式碼優化必定會花上很多時間(機器碼產生的速度很慢),但優化後的程式碼執行效率比較高,反過來說,大可完全不優化(機器碼產生的速度很快),但這程式碼執行效率就很低。
上面是 JIT 的概念,而 JIT 在 CLR 做的事情可以看參考資料 9
C++/CLI
來簡單寫一個 C++/CLI 的 hello world,並且觀察產生的 exe
首先,開一個熟悉的 C++ 專案

接下來設定參數,讓他從你認識的 C++ 變成 C++/CLI
如圖,Common Language Runtime Support 選 /clr

選完後,可以看到 Rerference 多了一個 lib,他就是提供 CLR 的 lib
另外還需設定 Conformance mode 為 No

寫以下程式碼
using namespace System;
void wmain()
{
const char16_t* unmanagedBuffer{ u"From unmanaged to managed!" };
String^ managedBuffer{ gcnew String((wchar_t*)unmanagedBuffer) };
Console::WriteLine("Value: {0}", managedBuffer);
Console::ReadLine();
return;
}
成功編譯與執行
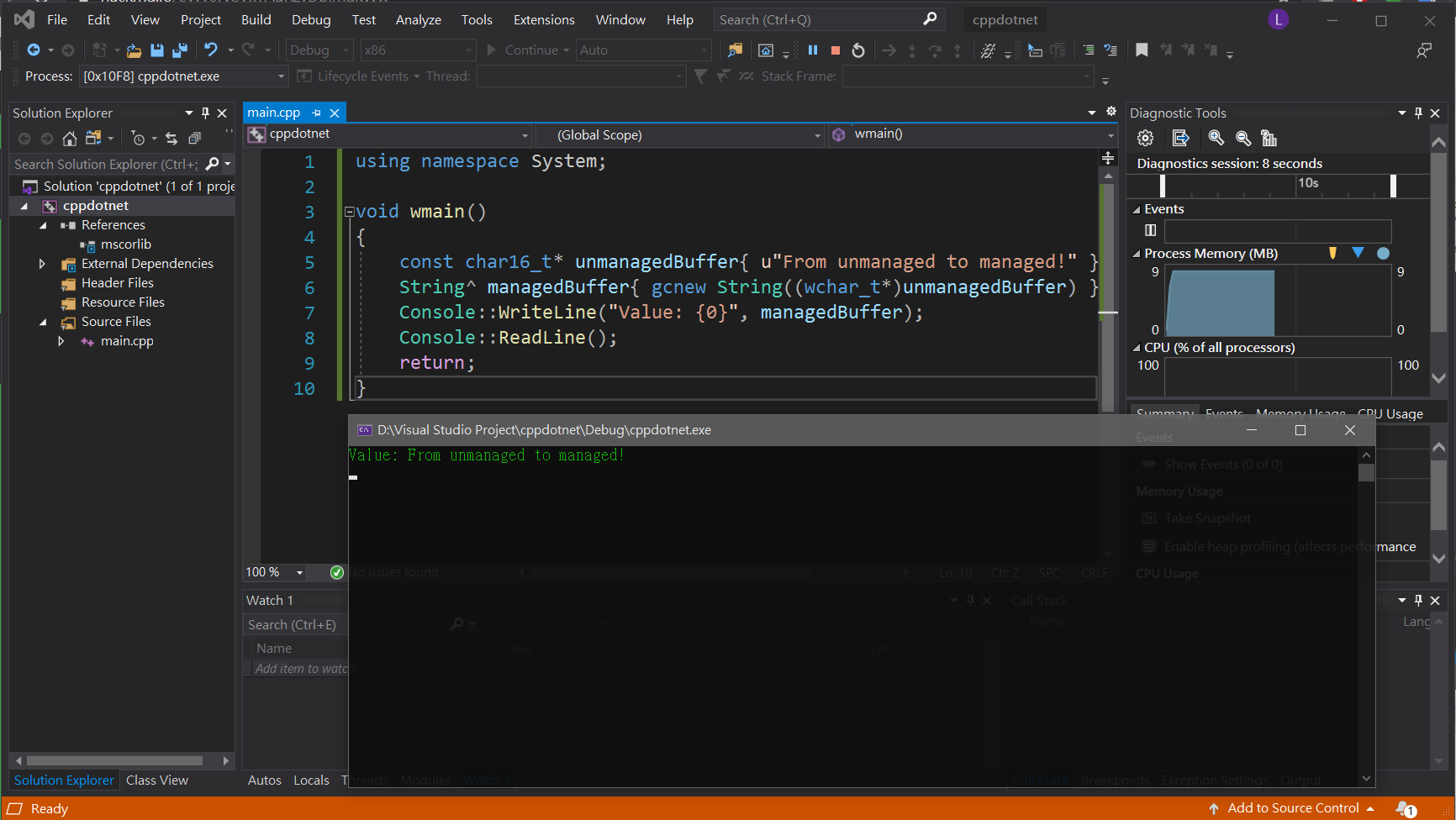
接下來就是看看 exe 長怎樣囉
用 IDA 開,會看到被 IDA 辨識為 Microsoft.NET assembly
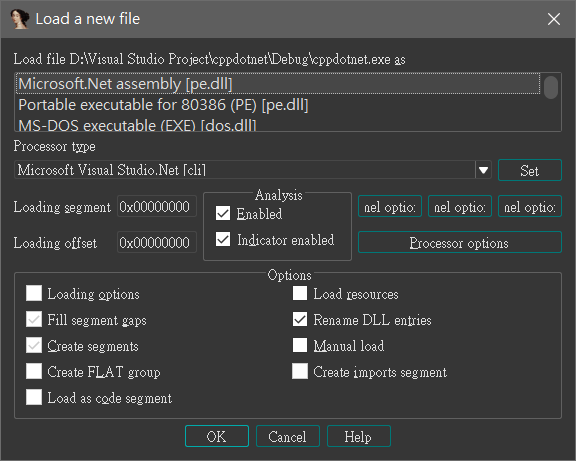
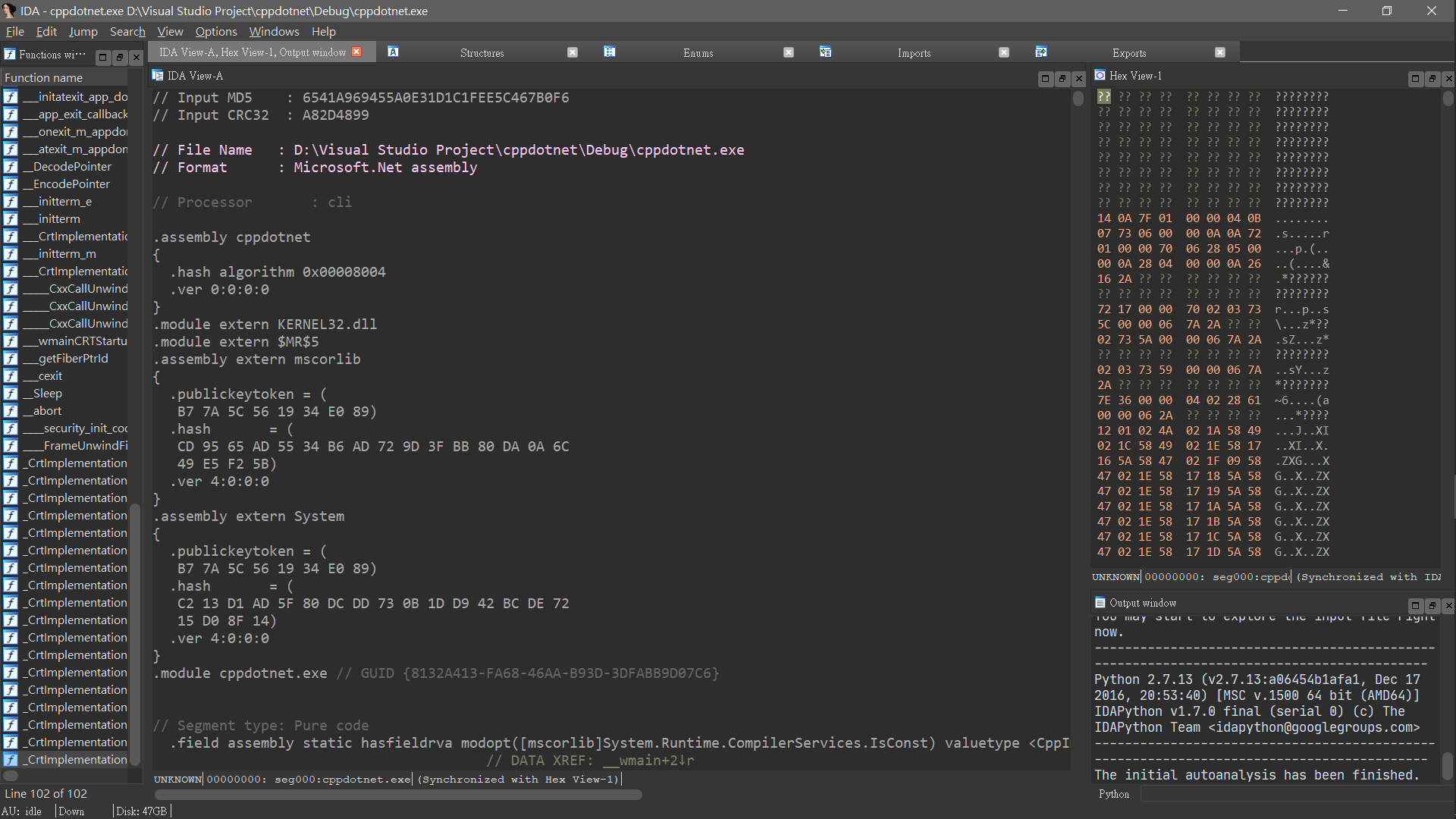
在以上的步驟後,生出的 exe 裡面放的已經不是原本熟知的 Machine code,而是變成 IL code
目前 (2020年6月) IDA 對於 IL code 相對其他語言來說支援度較低,這邊我們用一個內建的程式來觀察 IL code
執行圖中的 Developer Command Prompt for VS 2019
執行 ildasm (顧名思義,IL Disassembler)
把剛剛生出來的程式拖曳進去
拉到最下面,wmain 在最底下

點開來看

.method assembly static int32 modopt([mscorlib]System.Runtime.CompilerServices.CallConvCdecl)
wmain() cil managed
{
.vtentry 1 : 1
// Code size 34 (0x22)
.maxstack 2
.locals ([0] string managedBuffer,
[1] char modopt([mscorlib]System.Runtime.CompilerServices.IsConst)* unmanagedBuffer)
IL_0000: ldnull
IL_0001: stloc.0
IL_0002: ldsflda valuetype '<CppImplementationDetails>'.$ArrayType$$$BY0BL@$$CB_S modopt([mscorlib]System.Runtime.CompilerServices.IsConst) '?A0xfa77622d.unnamed-global-0'
IL_0007: stloc.1
IL_0008: ldloc.1
IL_0009: newobj instance void [mscorlib]System.String::.ctor(char*)
IL_000e: stloc.0
IL_000f: ldstr "Value: {0}"
IL_0014: ldloc.0
IL_0015: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string,
object)
IL_001a: call string [mscorlib]System.Console::ReadLine()
IL_001f: pop
IL_0020: ldc.i4.0
IL_0021: ret
} // end of method 'Global Functions'::wmain
可以看到 wmain 後面有 cli managed
好像還是很難看懂?
沒關係,還有一個工具 dnSpy
但我們晚點再用這個工具,我們先看另外一份 code
using namespace System;
using namespace System::Runtime::InteropServices;
[DllImport("msvcrt", CharSet=CharSet::Ansi)]
extern "C" int puts(String^);
typedef void* HWND;
[DllImport("user32", CharSet=CharSet::Ansi)]
extern "C" int MessageBox(HWND hWnd, String ^ pText, String ^ pCaption, unsigned int uType);
int main()
{
String^ pStr = "Hello World!";
String^ pCaption = "PInvoke Test";
puts(pStr);
MessageBox(0, pStr, pCaption, 0);
Console::ReadLine();
}
再來看看他的 exe
.method assembly static int32 modopt([mscorlib]System.Runtime.CompilerServices.CallConvCdecl)
main() cil managed
{
.vtentry 1 : 1
// Code size 41 (0x29)
.maxstack 4
.locals ([0] string pStr,
[1] string pCaption)
IL_0000: ldnull
IL_0001: stloc.0
IL_0002: ldnull
IL_0003: stloc.1
IL_0004: ldstr "Hello World!"
IL_0009: stloc.0
IL_000a: ldstr "PInvoke Test"
IL_000f: stloc.1
IL_0010: ldloc.0
IL_0011: call int32 puts(string)
IL_0016: pop
IL_0017: ldc.i4.0
IL_0018: ldloc.0
IL_0019: ldloc.1
IL_001a: ldc.i4.0
IL_001b: call int32 MessageBox(void*,
string,
string,
uint32)
IL_0020: pop
IL_0021: call string [mscorlib]System.Console::ReadLine()
IL_0026: pop
IL_0027: ldc.i4.0
IL_0028: ret
} // end of method 'Global Functions'::main
依舊有 cli managed
那 puts 跟 MessageBox 呢
.method public static pinvokeimpl("msvcrt" ansi winapi)
int32 puts(string A_0) cil managed preservesig
{
}
.method public static pinvokeimpl("user32" ansi winapi)
int32 MessageBox(void* hWnd,
string pText,
string pCaption,
uint32 uType) cil managed preservesig
{
}
兩個都多了 preservesig
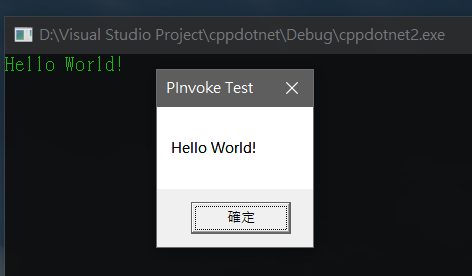
執行結果
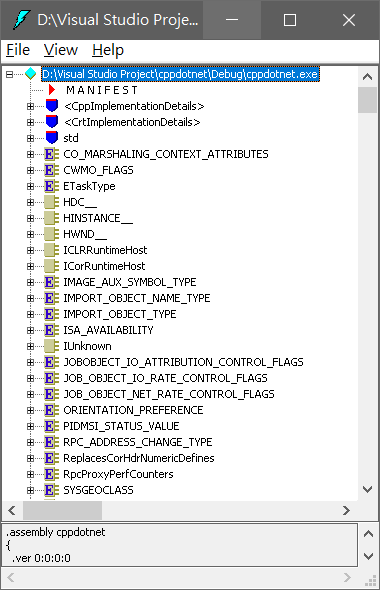
該來用 dnSpy 來看看了,首先把 exe 拖曳進去

點開旁邊的 <Module> 找到 main
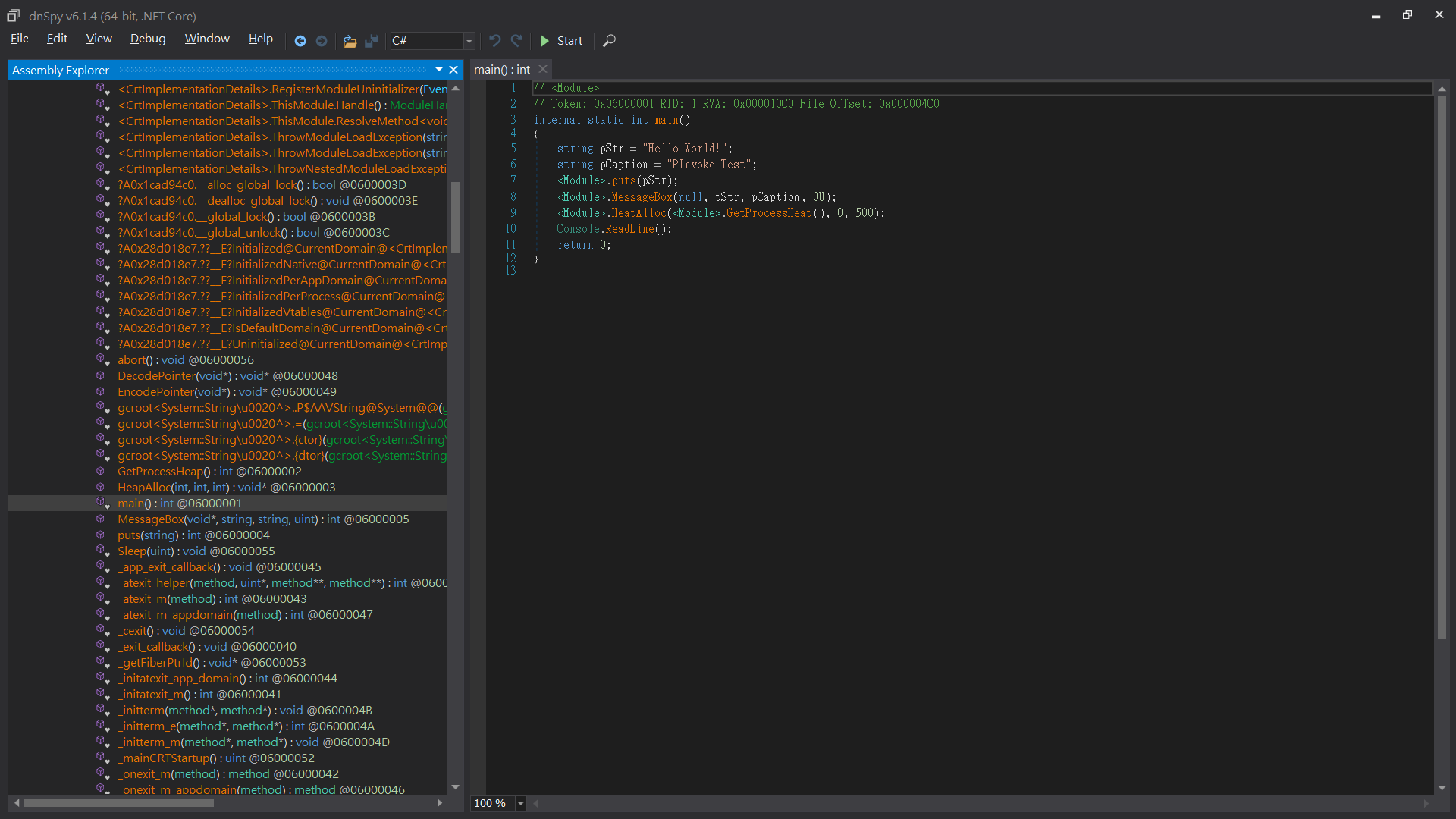
可以看到,幾乎完美的編回了原本的 C++/CLI code
且還提供了改 IL code 的功能

改完後
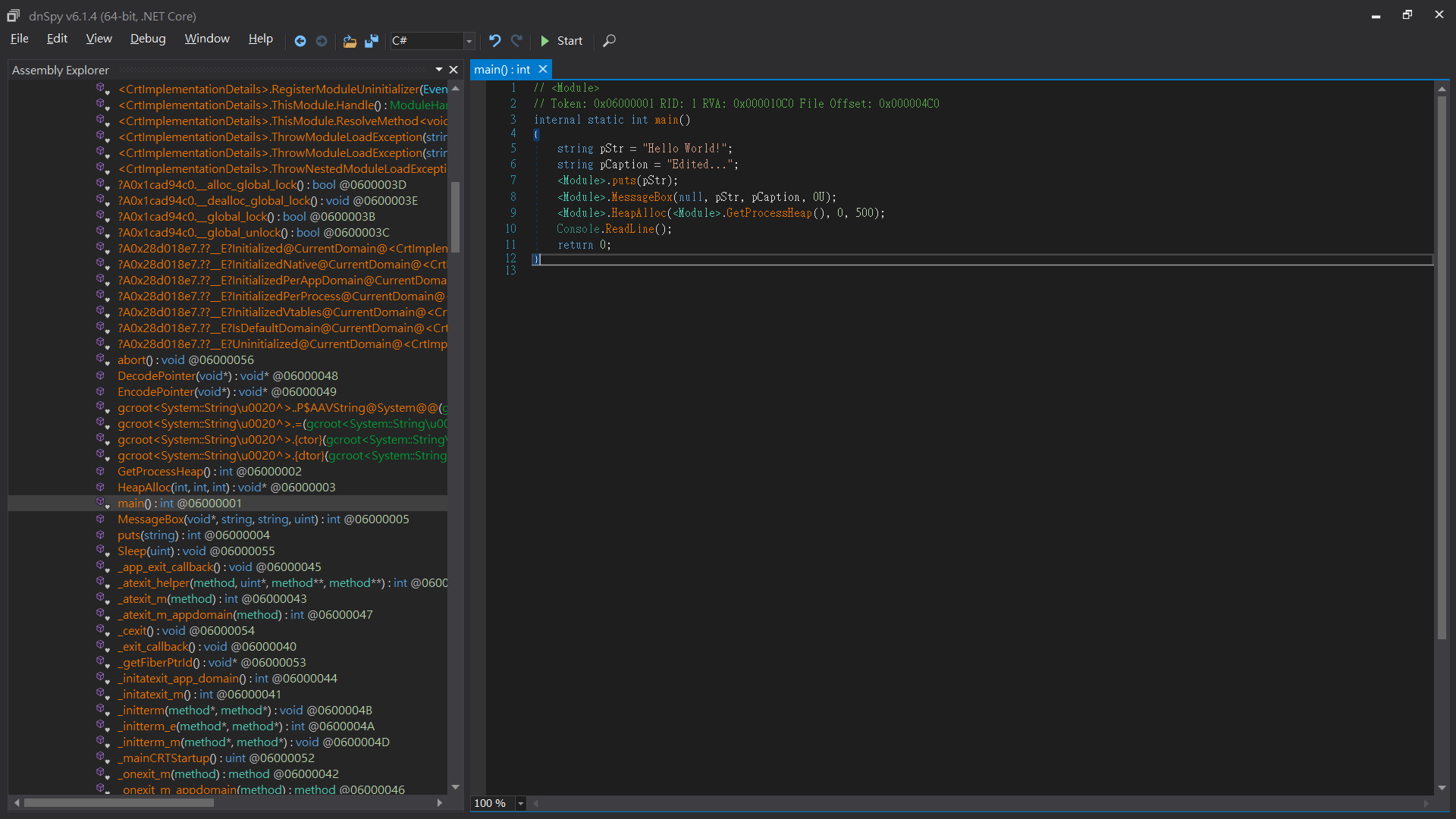
儲存起來 File > Save Module...,取消勾選 Save PDB File
執行看看
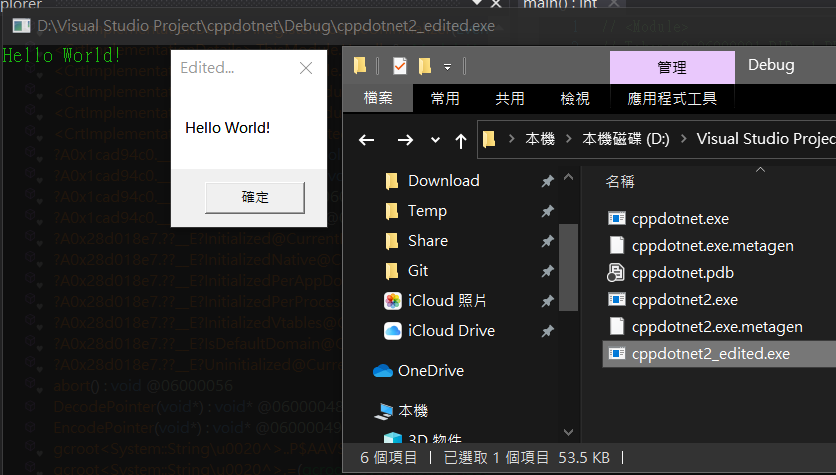
dnSpy 的功能非常強大,這邊開一個坑,之後有機會寫文章介紹實際使用過程
後記
這份筆記寫得有點雜亂,雖然叫做 .NET 筆記,但寫完後才發現講的東西好像都是 CIL 跟 CLR,之後有機會再擴充/修訂這篇筆記
原本只是想為最近 CTF 中遇到 .NET 惡意程式寫篇 write-up,但其實自己對於 .NET 可以說是沒有任何基礎知識,就先寫了這篇,寫完後果然學到不少東西
參考資料
- MSDN .NET 框架概述
- wiki .NET
- 簡介C#編譯成IL,再由JIT編譯成機器碼的過程
- CLR 相比 JVM有哪些先进之处?
- 通用語言架構
- wiki 即時編譯
- Ilasm.exe (IL Assembler)
- Anatomy of a .NET Assembly – PE Headers
- A look at the internals of ‘Tiered JIT Compilation’ in .NET Core
- Pro .NET Framework with the Base Class Library
- 一堆爬文